-Penis:
+The root: as its name indicated, this is the first part of the penis that attaches to the abdominal structures.
+The body:
- Looks like a cylinder.
- Contains three internal chambers (two large spaces called corpora cavernosa and smaller one called corpus spongiosum). There are spaces inside the body that are filled with blood when the pelvis becomes erect, rigid, and large.
- The skin is elastic which allows the penis to change size.
+The glans
- Cone-shaped.
- Covered by a layer of skin called foreskin which originated from the corona (base of the glans).
- The opening of the urethra (the tube that transports both semen and urine out of the body) is located here.
-Scrotum:
+Is a sac of skin that is located below the penis.
+Holds the testes (testicles), arteries, veins, and many nerves.
+Is responsible for protecting your testes under suitable temperature because testes must be at a lower temperature than the body temperature.
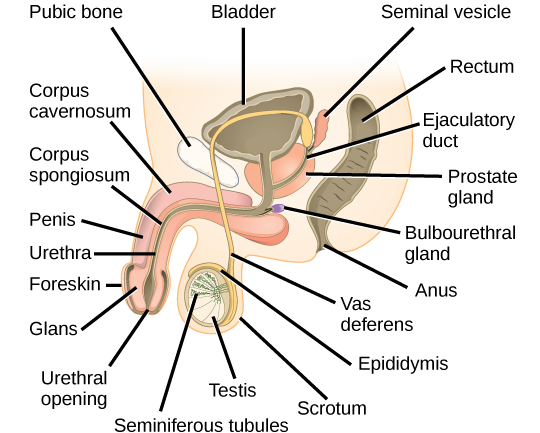
–Testes:
+Lies inside the scrotum
+Spermatic cord anchors the testes to the scrotum at either end.
+Most men have two testes (The left one usually hangs lower than the right one).
+Is responsible for making male sex hormone (testosterone) and producing sperm.
-Epididymis:
+Long coiled tube that is twenty feet in length which rests on each testicle.
+Provides an environment that allows sperm to be mature.
+Carries sperm into the vas deferens due to contractions force during sexual arousal.
-Vas deferens:
+Transports sperm from the epididymis.
+Connects the epididymis with the pelvic cavity.
+Located behind the bladder
+Transports mature sperm to the urethra in order to prepare for ejaculation
+The part of the vas deferens inside the scrotum was intertwined with blood vessels, and nerves (spermatic cord).
-Ejaculatory ducts:
+Fusion of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicles
+Lead to the urethra.
–Urethra:
+Carries urine from the bladder and semen (when reaching the organism) outside of your body.
+During an organism, urine is blocked from the urethra and only semen is forced out.
-Seminal vesicles:
+Attach to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder.
+Produce a special kind of food that provides sperm energy to move.
+Produce semen (sperm + seminal fluid).
-Prostate gland:
+Located below the bladder and in front of the rectum.
+Produces a kind of fluid that helps to nourish the sperm.
+Urethra runs through the center of the prostate gland.
-Couper’s glands (Bulbourethral glands):
+Located on the sides of the urethra, below the prostate gland.
+Produces a special, slippery, crystal fluid that runs into the urethra and lubricates it. The fluid also helps to neutralize any acidic it that may be present due to drops of urine in the urethra.